Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Takano, Masahiro*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 634, p.118673_1 - 118673_8, 2024/05
To investigate silicon effects on the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of iron, neutron diffraction and X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted to examine hcp-Fe Si
Si under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe
under high pressures and high temperatures. Neutron diffraction experiments were performed on the deuterated hcp-Fe Si
Si at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe
at 13.5 GPa and 900 K, and at 12.1 GPa and 300 K. By combining the P-V-T equation of state of hcp-Fe Si
Si , present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe
, present results indicate that the hydrogen-induced volume expansion of hcp-Fe Si
Si is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,
is 10% greater than that of pure hcp iron. Using the obtained values, we estimated the hydrogen content that would reproduce the density deficit in the inner core, which was 50% less than that without the effect of silicon. Possible hydrogen content,  , in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe
, in the inner core and the outer core was calculated to be 0.07 and 0.12-0.15, respectively, when reproducing the density deficit of the inner core with hcp-Fe Si
Si Hx.
Hx.
Yamamoto, Yusuke*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2023-003, 67 Pages, 2024/02
A long-term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios ( D,
D, 
 O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for
O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for  D and
D and 
 O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of
O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of  D and
D and 
 O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the
O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the  D and
D and 
 O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
Osawa, Hideaki
Gijutsushi "Chubu", (12), p.34 - 41, 2023/09
This introduces current status of Toki Geochronology Research Laboratory, Tono Geoscience Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Koike, Akari*; Nakashima, Risako*; Nemoto, Masaya*; Sakai, Takaaki*; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Due to global warming, the amount of snowfall in abnormal snowfall events may increase in the future. In order to evaluate the effect of global warming on the probability of exceeding the limit temperature at the core outlet as a core damage factor in a sodium-cooled fast reactor, a hazard curve of snowfall was developed considering global warming, and a dynamic PRA was performed. As a result, it was found that the amount of snowfall in abnormal snowfall events increases due to global warming, and the probability of exceeding the limit temperature increases.
Nakashima, Risako*; Koike, Akari*; Sakai, Takaaki*; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/08
In development of a quantitative risk assessment method to the external hazards for a sodium-cooled fast reactor, a dynamic PRA using the Continuous Markov chain Monte Carlo (CMMC) method was performed to evaluate the effect of global warming on the probability of exceeding the temperature limit as a core damage factor. There is a possibility that the amount of snowfall in abnormal snowfall events will increase due to global warming in the future. A hazard curve of snowfall considering global warming was developed. The results show that the probability of exceeding the temperature limit is increased by the abnormal snowfall events due to global warming.
Hattori, Takanori
Yukuatsu Gijutsu, 61(7), p.29 - 35, 2022/07
As an example of the application of hydraulic technology, the 6-axis type multi-anvil press "ATSUHIME" in the J-PARC ultra-high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET and the research on hydrogen in the Earth's core using them are introduced.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamasaki, Shinya*
Chikyu Kagaku, 55(4), p.93 - 95, 2021/12
Ten years have passed since the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident. In this special issue, we compiled review papers on the environmental behavior of the FDNPP-derived radionuclides from various research fields. This special issue shows that various research fields contributed to better understandings on the environmental behavior of the FDNPP-derived radionuclides.
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Koike, Katsuaki*
Joho Chishitsu, 32(3), P. 95, 2021/09
We received best presentation award GEOINROUM-2021 for the presentation on "Estimation of contaminated materials concentration by a geostatistical method with groundwater flow". We submit the comments of impression for getting the Award to Geoinformatics.
Iizuka, Riko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Shito, Chikara*; Fukuyama, Ko*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12632_1 - 12632_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The Earth's core consist of Fe-Ni alloy with some light elements (H, C, O, Si, S etc.). Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe and one of the promising candidates. In this study, we have investigated the effects of sulfur(S) on hydrogenation of iron-hydrous silicate system containing saturated water in the ideal composition of the primitive Earth. We observed a series of phase transitions of Fe, dehydration of the hydrous mineral, and formation of olivine and enstatite with increasing temperature. The FeS formed as the coexisting phase of Fe under high-pressure and temperature condition, but its unit cell volume did not increase, suggesting that FeS is hardly hydrogenated. Recovered samples exhibited that H and S can be incorporated into solid Fe, which lowers the melting temperature as Fe(H )-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
)-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
Onoe, Hironori; Kosaka, Hiroshi*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yasue, Kenichi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.3 - 14, 2019/06
In this study, it is focused on topographic changes due to uplift and denudation, also climate perturbations, a method which is able to assess the long-term variability of groundwater flow conditions using the coefficient variation based on some steady-state groundwater flow simulation results was developed. Spatial distribution of long residence time area which is not much influenced due to long-term topographic change and recharge rate change during the past one million years was able to estimate through the case study of the Tono area, Central Japan. By applying this evaluation method, it is possible to identify the local area that has low variability of groundwater flow conditions due to topographic changes and climate perturbations from the regional area quantitatively and spatially.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari
JAEA-Conf 2018-013, p.13 - 16, 2019/02
In the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA-AMS-TONO was introduced in March 1997 and it will be the 20th year in this year. After introduction, we maintained the carbon-14 measurement first and we were able to steadily accumulate results.
Mezawa, Tetsuya; Mochizuki, Akihito; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-001, 55 Pages, 2018/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting "geoscientific study" and "research and development on geological disposal" in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) for safe geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Geochemical parameters of groundwater pressure, pH, and oxidation-reduction potential in the deep groundwater has been continuously monitored with monitoring systems which were developed in the Horonobe URL Project. This report presents the physico-chemical parameters of groundwater which have been obtained by the monitoring systems installed at the 140 m, 250 m and 350 m gallery. The data obtained until March 31, 2017 was summarized along with related information such as the specifications of boreholes and the excavation of the URL.
 neutron diffraction of iron hydride in iron-silicate-water system under high pressure and high temperature condition
neutron diffraction of iron hydride in iron-silicate-water system under high pressure and high temperature conditionIizuka, Riko*; Yagi, Takehiko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami
Hamon, 27(3), p.104 - 108, 2017/08
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the solar system and is considered to be one of the promising candidates of the light elements in the Earth's core. However, the amount of hydrogen dissolved in the core and its process are still unknown because hydrogen cannot be detected by X ray and easily escapes from iron at ambient conditions. In this study, we have conducted high-pressure and high-temperature in-situ neutron diffraction experiments on the iron-hydrous mineral system using PLANET in J-PARC. We observed that the water, which was dissociated from a hydrous mineral, reacted with iron to form both iron oxide and iron hydride at about 4 GPa. Iron hydride remained stable after further increase in temperature. This formation occurred at 1000K, where no materials melted. This suggests that hydrogen dissolved into iron before any other light elements dissolved in the very early stage of the Earth's evolution.
Iizuka, Riko*; Yagi, Takehiko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami
Nature Communications (Internet), 8, p.14096_1 - 14096_7, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:88.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Density of the Earth's core is lower than that of pure iron and the light element(s) in the core is a long-standing problem. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the solar system and thus one of the important candidates. However, the dissolution process of hydrogen into iron remained unclear. Here we carry out high-pressure and high-temperature in situ neutron diffraction experiments and clarify that when the mixture of iron and hydrous minerals are heated, iron is hydrogenized soon after the hydrous mineral is dehydrated. This implies that early in the Earth's evolution, as the accumulated primordial material became hotter, the dissolution of hydrogen into iron occurred before any other materials melted. This suggests that hydrogen is likely the first light element dissolved into iron during the Earth's evolution and it may affect the behaviour of the other light elements in the later processes.
Tomioka, Naotaka*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Purevjav, N.*; Abe, Jun*; Harjo, S.
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 43(4), p.267 - 275, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions
C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutionsWalker, C.; Suto, Shunkichi; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Cement and Concrete Research, 79, p.1 - 30, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:90.42(Construction & Building Technology)Modeling the solubility behavior of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel is important to make quantitative predictions of the degradation of hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) based materials. Experimental C-S-H gel solubility data have been compiled from the literature, critically evaluated and supplemented with new data from the current study for molar Ca/Si ratios = 0.2-0.83. All these data have been used to derive a discrete solid phase (DSP) type C-S-H gel solubility model based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions in aqueous solution(SSAS). Features of the DSP type C-S-H gel solubility model include satisfactory predictions of pH values and Ca and Si concentrations for all molar Ca/Si ratios = 2.7  0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios
0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios  1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO
1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO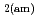 ) for Ca/Si ratios
) for Ca/Si ratios  0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
Koike, Katsuaki*; Kubo, Taiki*; Liu, C.*; Masoud, A.*; Amano, Kenji; Kurihara, Arata*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Lanyon, B.*
Tectonophysics, 660, p.1 - 16, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:66.63(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This study integrates 3D models of rock fractures from different sources and hydraulic properties aimed at identifying relationships between fractures and permeability. A geostatistical method (GEOFRAC) that can incorporate orientations of sampled data was applied to 50,900 borehole fractures for spatial modeling of fractures over a 12 km by 8 km area, to a depth of 1.5 km. GEOFRAC produced a plausible 3D fracture model, in that the orientations of simulated fractures correspond to those of the sample data and the continuous fractures appeared near a known fault. Small-scale fracture distributions with dominant orientations were also characterized around the two shafts using fracture data from the shaft walls. By integrating the 3D model of hydraulic conductivity using sequential Gaussian simulation with the GEOFRAC fractures from the borehole data, the fracture sizes and directions that strongly affect permeable features were identified.
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Omori, Kazuaki; Munemoto, Takashi; Onoe, Hironori
Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(4), p.3041 - 3057, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.36(Environmental Sciences)Changes of hydrochemical condition resulting from large-scale underground facility construction to 500 m depth in sedimentary and granitic rock were evaluated at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), Japan. The investigation of hydrochemical impact around the facility suggests that an understanding of hydrogeological structures, including hydrogeological compartments prior to facility construction and the locating of shafts/galleries in low permeability rock area is essential to minimize hydrochemical disturbances.
Suzuki, Takashi; Kitamura, Toshikatsu; Kabuto, Shoji*; Togawa, Orihiko; Amano, Hikaru
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(11), p.1431 - 1435, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English